Choosing a life insurance policy is one of the most critical financial decisions you'll make, yet the landscape is filled with complex terms and competing options. From the straightforward affordability of Term Life to the investment potential of a Variable Universal Life policy, finding the right coverage can feel overwhelming. The truth is, there is no single "best life insurance policy" for everyone. The ideal choice is deeply personal and depends entirely on your specific circumstances, including your age, financial goals, family needs, and personal risk tolerance.
This guide is designed to demystify the process. We will break down the 10 most common types of life insurance, providing a clear and comprehensive comparison. For each policy, we will explore its core features, unique advantages, and potential drawbacks. Instead of a one-size-fits-all answer, you'll gain the clarity needed to identify the policy that aligns perfectly with your life's roadmap. Our goal is to provide you with a framework for making a confident and informed choice that secures your family's future and offers genuine peace of mind.
We'll dive into real-world scenarios, offer actionable insights, and present a structured overview of what each option entails. This ensures you can confidently navigate your options, whether you're a self-employed professional, a pre-retiree, or a parent planning for your children's security. Beyond selecting the right policy, it's also important for beneficiaries to know what to expect later, and understanding the life insurance claim process is crucial for ensuring a smooth payout when it's most needed. This comprehensive roundup will equip you with the knowledge to select the best life insurance policy for your unique situation.
1. Term Life Insurance
Term life insurance is the most straightforward and affordable type of life insurance, making it a popular choice for families and individuals seeking financial protection. This policy provides coverage for a specific period, known as the "term," which typically lasts 10, 20, or 30 years. If the insured person passes away during this term, the policy pays a tax-free death benefit to their beneficiaries.
Because it is pure protection with no savings or investment component (known as cash value), its premiums are significantly lower than permanent life insurance. The primary purpose is to replace lost income during crucial years, such as when you are raising children, paying off a mortgage, or building a business. If you outlive the policy's term, it simply expires, and no benefit is paid.
When to Choose Term Life Insurance
This type of policy is ideal for covering financial responsibilities with a clear end date. For instance, a young couple with a new 30-year mortgage might purchase a 30-year term policy to ensure the surviving partner can pay off the house. Similarly, parents of young children often choose a 20-year term to provide a financial safety net until their kids are financially independent.
For a quick reference, the infographic below highlights the core features that define a term life insurance policy.
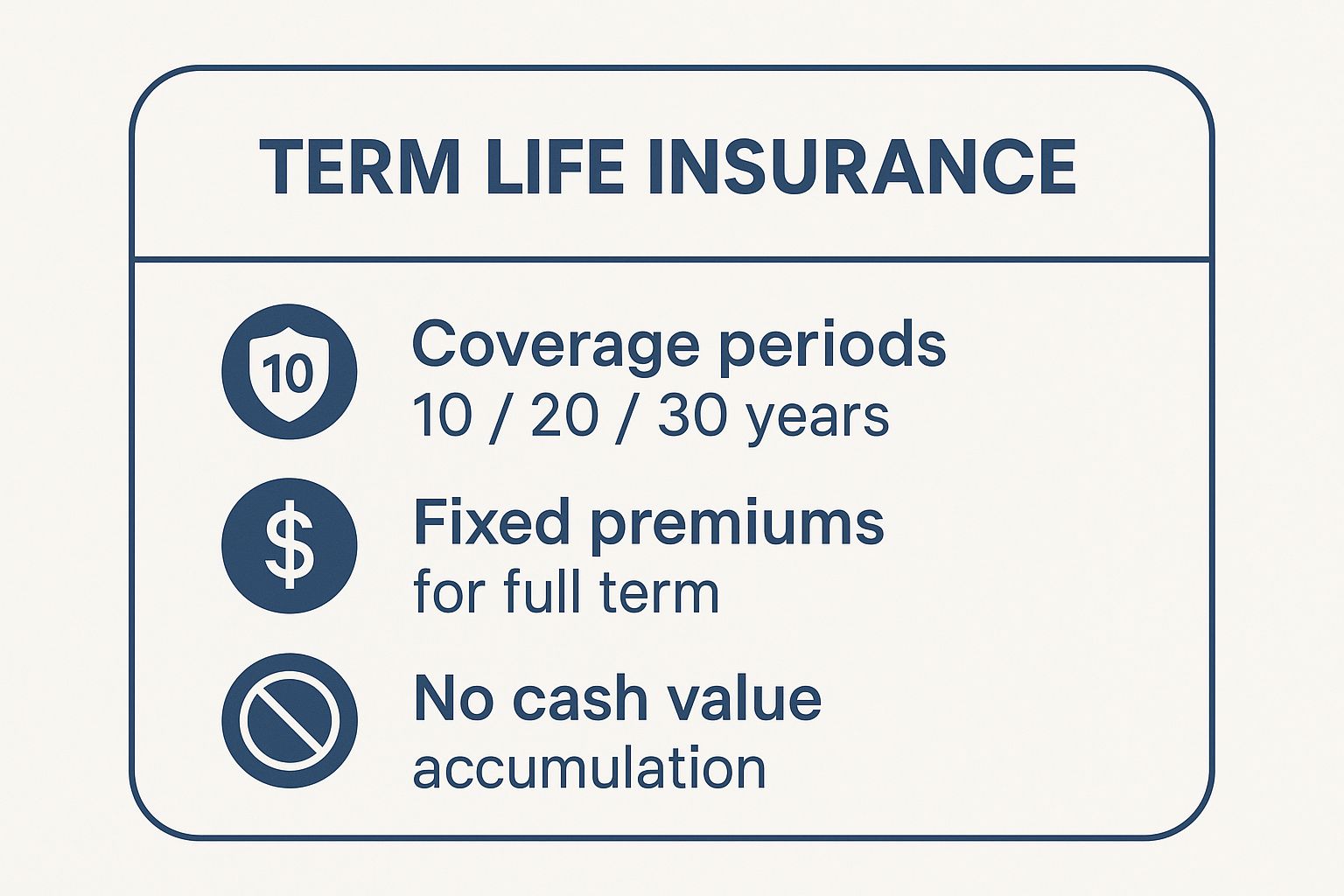
The key takeaway is simplicity: you get locked-in premiums for a set coverage period without the complexity of a cash value account. This makes it a powerful and cost-effective tool for targeted financial protection.
Actionable Tips for Policyholders
To maximize the value of your policy, consider these strategies:
- Choose the Right Term: Align your term length with your longest financial obligation. If your mortgage has 27 years left, a 30-year term is a safe bet.
- Calculate Coverage Needs: A common guideline is to secure coverage worth 10 to 15 times your annual income.
- Consider Convertibility: A convertible term policy allows you to convert to a permanent policy later without a new medical exam, offering crucial flexibility if your needs change.
- Shop Around: Premiums can vary significantly between insurance carriers for the exact same coverage, so comparing quotes is essential to finding the best life insurance policy for your budget.
For families looking to expand coverage efficiently, adding a rider can be a smart move. Learn more about adding a spouse term rider to see how you can cover both partners under one primary policy.
2. Whole Life Insurance
Whole life insurance is a type of permanent life insurance designed to provide coverage for your entire life, as long as premiums are paid. Unlike term insurance, it combines a death benefit with a savings component, known as "cash value," which grows at a guaranteed, tax-deferred rate. This creates a policy that offers both lifelong protection and a financial asset.
Because it includes this cash value element and lasts a lifetime, premiums are significantly higher than term life insurance. A portion of each premium funds the death benefit, while the rest contributes to the cash value. This account can be borrowed against or withdrawn from, providing a source of liquidity for financial emergencies or opportunities.

When to Choose Whole Life Insurance
This policy is best suited for individuals with long-term financial goals who have already maximized other investment vehicles like a 401(k) or IRA. It is a powerful tool for estate planning, allowing high-net-worth individuals to create a tax-free inheritance for their heirs. Business owners also use the cash value as a stable source of emergency funding, while others use it to leave a guaranteed financial legacy for their loved ones.
The key takeaway is predictability: you get locked-in premiums, a guaranteed death benefit, and guaranteed cash value growth. This makes it a conservative and reliable component of a diversified financial portfolio.
Actionable Tips for Policyholders
To ensure your whole life policy serves your financial goals effectively, consider these strategies:
- View it as a Long-Term Commitment: Whole life insurance builds significant cash value over decades. Plan to hold the policy for at least 15 to 20 years to see substantial growth.
- Prioritize High-Rated Carriers: Look for policies from financially strong, mutually owned insurance companies that have a history of paying dividends, which can accelerate your cash value growth.
- Utilize a Paid-Up Additions Rider: This rider allows you to use policy dividends to purchase small, additional "paid-up" policies, compounding your death benefit and cash value growth over time.
- Understand Surrender Charges: Be aware of the surrender period and associated fees, which can be high if you cancel the policy in its early years.
For those looking to find the best life insurance policy for their specific needs, it's crucial to compare illustrations from multiple providers. To see a detailed comparison of top carriers, you can explore the best whole life insurance policies and find the right fit for your long-term strategy.
3. Universal Life Insurance
Universal life (UL) insurance is a type of permanent life insurance that offers more flexibility than whole life. This policy provides a death benefit alongside a cash value component that earns interest based on current market rates. Its key feature is the ability for policyholders to adjust their premium payments and death benefit amounts within certain limits.
UL insurance separates the insurance cost (cost of insurance) from the savings component, providing transparency into how your premiums are allocated. This design allows you to pay more into the policy when you can to build cash value faster or pay the minimum premium to simply keep the coverage in force. Because the interest credited to the cash value is tied to market performance, it offers greater growth potential than whole life but also comes with less certainty.
When to Choose Universal Life Insurance
This type of policy is ideal for those who need lifelong coverage but also want the flexibility to adapt their policy to changing financial circumstances. For example, a self-employed professional with a variable income can pay higher premiums during profitable years and lower ones during leaner times. It's also a valuable tool for middle-aged professionals who want to use the cash value growth to supplement retirement income down the road.
The main advantage is adaptability. You can increase the death benefit during peak earning years to protect your family and later reduce it in retirement when your financial obligations decrease. This flexibility makes it a versatile choice for finding the best life insurance policy for long-term, evolving needs.
Actionable Tips for Policyholders
To maximize the value of your universal life policy, consider these strategies:
- Fund Generously Early On: Overfunding the policy in the early years builds a strong cash value cushion that can help cover premium costs later if needed.
- Review Policy Annually: Meet with your agent each year to review your policy's performance. Ensure the cash value is growing as projected and the policy is not in danger of lapsing.
- Understand Illustrations Conservatively: When reviewing policy illustrations, ask for projections based on lower, more conservative interest rate assumptions to avoid surprises if market rates decline.
- Know Your Minimum Premium: Be aware of the minimum premium required to keep your policy active. Consistently paying only the minimum can deplete your cash value and cause the policy to lapse.
4. Guaranteed Universal Life Insurance (GUL)
Guaranteed Universal Life (GUL) insurance offers a middle ground between term and whole life, providing permanent, lifelong coverage with more affordable, fixed premiums. This policy is often called "term for life" because it strips away the complex cash value accumulation of other permanent policies, focusing solely on guaranteeing a death benefit, typically up to age 121.
Unlike other universal life policies with flexible premiums that can lapse if the cash value underperforms, a GUL’s guarantee is tied directly to paying the fixed premium on time. This makes it the most cost-effective way to secure a permanent death benefit without the high costs associated with whole life or the investment risks of other universal life products. It is purely designed for protection, not as a savings or investment vehicle.
When to Choose Guaranteed Universal Life Insurance
This type of policy is ideal for those who need coverage for their entire life but do not want or need to pay for a cash value component. For example, a 60-year-old might purchase a GUL policy to cover potential estate taxes, ensuring their heirs receive their full inheritance. Business owners also use GUL to fund buy-sell agreements, guaranteeing the business can continue operating smoothly after a partner's death at a lower cost than whole life.
It's also a powerful tool for anyone who wants to ensure funds are available for final expenses or leave a guaranteed inheritance to children or a charity. The key is its predictability: you know exactly what you need to pay to keep the lifelong coverage active, making it one of the best life insurance policy options for long-term planning.
Actionable Tips for Policyholders
To maximize the value of your policy, consider these strategies:
- Ensure a Lifetime Guarantee: For true permanent coverage, choose a policy that guarantees coverage to age 120 or 121.
- Never Miss a Premium: The "no-lapse" guarantee is contingent on timely payments. A single missed payment can put the entire policy at risk.
- Compare Carrier Pricing: Premiums for GUL policies vary significantly between insurers. Shopping around is crucial to secure the most competitive rate.
- Leverage for Estate Planning: A GUL policy is an excellent, cost-effective tool to fund an Irrevocable Life Insurance Trust (ILIT), which can help pass wealth to heirs tax-free.
5. Variable Universal Life Insurance (VUL)
Variable Universal Life (VUL) insurance is a type of permanent life insurance that offers a death benefit alongside a separate cash value account with investment sub-accounts. This structure gives policyholders the potential for greater cash value growth by investing directly in the market, similar to mutual funds. Unlike other permanent policies, you control how the cash value is allocated among these investment options, which can include stocks, bonds, and money market funds.
The policy's main appeal is its high growth potential and flexibility. Premiums are adjustable, and the death benefit can also be modified to fit changing needs. However, this flexibility comes with market risk. The cash value and potentially the death benefit can fluctuate based on the performance of your chosen investments. A poor market performance can reduce your cash value and may require higher premium payments to keep the policy active.
When to Choose Variable Universal Life Insurance
This policy is best suited for individuals with a high-risk tolerance and a sophisticated understanding of investments who are looking to maximize tax-advantaged growth. It is often used by high-income professionals or entrepreneurs who have already maxed out other retirement accounts like a 401(k) and IRA. VUL can also serve as a powerful estate planning tool for wealthy individuals, offering a way to grow wealth that can be passed on to heirs tax-free.
For a clearer understanding of how VUL combines insurance and investments, the video below offers a detailed explanation.
The key takeaway is control: VUL provides the ultimate flexibility in managing both premiums and the investment component of a life insurance policy, making it a powerful tool for savvy investors.
Actionable Tips for Policyholders
To effectively manage a VUL policy and mitigate its inherent risks, consider these strategies:
- Understand the Risks: Only consider this policy if you are comfortable with market volatility and the potential for loss.
- Over-fund the Policy: Pay more than the minimum premium, especially in the early years, to build a cash value cushion that can absorb market downturns without jeopardizing your coverage.
- Diversify Your Investments: Spread your cash value across various sub-accounts to manage risk, just as you would with a standard investment portfolio.
- Monitor and Rebalance: Review your sub-account performance quarterly and rebalance annually to align with your long-term financial goals and risk tolerance.
- Work with a Fee-Based Advisor: Partner with a financial professional who is not solely commission-based to receive objective advice on finding the best life insurance policy for your complex financial situation.
6. Indexed Universal Life Insurance (IUL)
Indexed Universal Life (IUL) insurance is a type of permanent life insurance that offers a unique balance between safety and growth. Its cash value growth is linked to a stock market index, like the S&P 500, allowing policyholders to participate in market gains. However, it also includes a "floor," typically 0%, which protects the cash value from losing money during market downturns.
This structure positions IUL as a hybrid, offering more growth potential than a traditional whole life or universal life policy but with less risk than a variable universal life policy. Interest is credited to the cash value based on the index's performance, but this growth is often subject to a "cap" (a maximum rate of return) and a "participation rate" (the percentage of the index's gain that is credited to your policy).
When to Choose IUL Insurance
IUL is often a good fit for individuals seeking long-term, tax-advantaged wealth accumulation with a safety net. It can be particularly effective for pre-retirees looking to supplement their retirement income with tax-free policy loans or withdrawals. Business owners also use IUL for key person insurance, benefiting from the growth potential while protecting against market losses. It's a strategic tool for those who have already maxed out other retirement accounts like a 401(k) or IRA.
The key takeaway is that IUL offers a way to capture some of the stock market's upside potential without being directly exposed to its downside risk. This makes it a compelling option for those looking for a long-term financial instrument that combines death benefit protection with cash value growth.
Actionable Tips for Policyholders
To effectively use an IUL policy, consider these strategies:
- Scrutinize Illustrations: Be skeptical of illustrations that project consistently high returns. Ask for projections using more conservative assumptions to understand the policy's performance in less-than-ideal scenarios.
- Understand Growth Mechanics: Get clarity on how caps, participation rates, and spreads work. These factors directly impact your cash value growth and can be adjusted by the insurer.
- Over-fund the Policy Early: Contribute more than the minimum premium in the early years to build a strong cash value foundation, which helps the policy perform better over the long term.
- Conduct Annual Reviews: Compare your policy's actual performance against the initial illustration each year. This helps you track its progress and make any necessary adjustments to your funding strategy.
For those considering this path, it's crucial to find a policy that balances competitive growth potential with reasonable costs. Comparing IUL options from carriers like National Life Group can provide insight into how different products structure their index crediting strategies.
7. Final Expense Life Insurance (Burial Insurance)
Final expense life insurance, often called burial insurance, is a type of whole life policy designed to cover end-of-life costs. These policies offer smaller death benefits, typically between $5,000 and $25,000, intended to pay for funeral services, cremation, medical bills, and other outstanding debts, preventing family members from facing a financial burden during a difficult time.
The primary appeal of final expense insurance is its accessibility. Most policies feature simplified or guaranteed issue underwriting, which means applicants can often get coverage without a medical exam and by answering only a few health questions. Because it is a form of permanent insurance, the premiums never increase, and the coverage never expires as long as payments are made, making it a reliable choice for seniors.
When to Choose Final Expense Life Insurance
This type of policy is ideal for seniors or individuals with significant health conditions who may not qualify for a traditional term or whole life policy. For example, a 75-year-old with pre-existing health issues could secure a $15,000 policy to ensure their funeral costs are covered. It is also an excellent option for those with limited savings who want to pre-plan and pre-fund their final arrangements without burdening their children.
The main takeaway is that final expense insurance provides peace of mind with a straightforward application process and affordable premiums. It serves a specific, crucial need by ensuring funds are available exactly when they are needed for final arrangements, making it one of the best life insurance policy options for this niche.
Actionable Tips for Policyholders
To ensure you get the most value from a final expense policy, consider these strategies:
- Calculate Your Needs: Research average funeral costs in your area, which typically range from $7,000 to $12,000, and choose a death benefit that comfortably covers those expenses.
- Understand Waiting Periods: Guaranteed issue policies often come with a two or three-year waiting period. If you pass away from natural causes during this time, your beneficiaries usually receive a refund of premiums plus interest rather than the full death benefit.
- Choose the Right Underwriting: If you have only minor health issues, apply for a 'simplified issue' policy. You may get a better rate and immediate coverage from day one.
- Keep Beneficiaries Informed: Make sure your beneficiaries know about the policy and have access to the documents to ensure a smooth and timely claim process.
For those planning for their end-of-life expenses, understanding the nuances of these policies is critical. Learn more about how final expense insurance works to see if it aligns with your financial goals.
8. Group Life Insurance (Employer-Sponsored)
Group life insurance is a form of coverage offered by an employer or large-scale entity to its workers or members. Typically included as part of an employee benefits package, it is often provided at a low cost or even for free. This convenience and affordability make it a valuable perk, offering a foundational layer of financial security for millions of employees.
The coverage amount is usually a multiple of the employee's annual salary, such as one or two times their income, or a set flat amount. A key advantage is its "guaranteed issue" nature, meaning employees can get coverage without a medical exam or answering health questions. This accessibility is crucial for individuals who might otherwise struggle to find an affordable policy due to pre-existing health conditions.

When to Choose Group Life Insurance
This policy is best viewed as a supplemental benefit rather than a primary source of life insurance. It's an excellent, no-cost starting point for anyone with a job that offers it. For example, an employee with diabetes who might face high premiums on the individual market can instantly secure guaranteed coverage through their employer.
However, since the coverage is often limited and tied to employment, it’s rarely sufficient on its own. A professional should use their employer's basic coverage as a safety net while purchasing a private term policy to cover the full scope of their financial obligations, like a mortgage or children's education. The key is to leverage the free benefit without becoming solely reliant on it.
Actionable Tips for Policyholders
To make the most of your employer-sponsored plan, consider these strategies:
- View It as a Supplement: Treat your group policy as a bonus, not your main coverage. Calculate your actual needs, which are often 10 to 15 times your income, and buy a private policy for the remaining amount.
- Understand Portability: Know what happens to your coverage if you leave your job. Some plans offer a "portability" option that lets you take the coverage with you, but often at a much higher premium.
- Check Conversion Privileges: Ask if your group policy can be converted into an individual whole life policy upon leaving the company. This can be a valuable option if your health has changed.
- Don't Postpone Private Coverage: Buy an individual policy when you are young and healthy. Relying only on your employer's plan can leave you uninsured if you change jobs or your health declines.
By combining a free or low-cost group policy with a robust individual plan, you can build a comprehensive strategy to find the best life insurance policy for your family's needs.
9. No Medical Exam Term Life Insurance (Simplified Issue)
No medical exam term life insurance, also known as simplified issue, offers a streamlined path to securing coverage without the traditional in-person medical exam. This policy provides term life benefits by evaluating your risk based on a detailed health questionnaire and data from third-party sources, such as prescription drug histories and motor vehicle records. The entire process is designed for speed and convenience, bypassing the need for blood tests or urine samples.
Because it eliminates the paramedical exam, the approval process shrinks from several weeks to just a few days, or in some cases, minutes. The primary trade-off for this convenience is that coverage amounts are often capped, typically at $1 million or less, and premiums may be slightly higher than a fully underwritten policy. It’s a powerful option for those who prioritize a quick and non-invasive application.
When to Choose No Medical Exam Life Insurance
This type of policy is ideal for individuals who need coverage fast or have an aversion to medical exams. For example, a healthy 35-year-old who needs to secure a policy before an international trip can get approved online in one day. It's also a great fit for busy professionals who find it difficult to schedule a medical appointment, allowing them to complete the entire application during a lunch break.
Its simplicity and speed make it one of the best life insurance policy options for healthy applicants seeking moderate coverage amounts without the typical waiting period. This convenience has made it a popular choice offered by modern insurers like Haven Life, Ladder Life, and Bestow.
Actionable Tips for Policyholders
To ensure you get the most out of this convenient option, consider these strategies:
- Be Completely Honest: Answer all health questions truthfully. Insurers will verify your information, and any misrepresentation can lead to a denied claim during the contestability period.
- Compare with Fully Underwritten: If you are in excellent health, get a quote for a traditional policy. A medical exam could qualify you for preferred rates and significant long-term savings.
- Understand the Data Check: Be aware that insurers will access your prescription history, MIB (Medical Information Bureau) report, and driving record as part of the underwriting process.
- Shop Multiple Providers: Not all simplified issue policies are the same. Rates, coverage limits, and underwriting criteria vary widely between carriers, so comparison shopping is crucial.
For those who want to explore this option further, understanding the nuances is key. You can discover more about no medical exam life insurance policies to see if it aligns with your specific needs and financial goals.
10. Return of Premium (ROP) Term Life Insurance
Return of Premium (ROP) term life insurance is a unique hybrid policy that blends the protection of term life with a money-back guarantee. It provides a death benefit if you pass away during a specific term, typically 20 or 30 years, just like standard term insurance. However, if you outlive the policy, the insurer refunds 100% of the premiums you paid, tax-free.
This feature addresses a common hesitation with term life: the feeling that premiums are "wasted" if you don't use the policy. In exchange for this guarantee, ROP policies have significantly higher premiums than their standard counterparts. The core idea is to provide life insurance coverage that is essentially free if you survive the term, making it a compelling option for those seeking certainty.
When to Choose ROP Term Life Insurance
This type of policy is ideal for individuals who are risk-averse, have strong cash flow, and value a guaranteed return over potential market gains. It can function as a form of "forced savings" for those who lack the discipline to invest the premium difference themselves. For example, a 35-year-old might pay $150 per month for a 20-year ROP policy, receiving a lump sum of $36,000 at age 55 if they are still living.
ROP is also a strong candidate for high-income earners who have already maxed out other tax-advantaged savings vehicles like a 401(k) or Roth IRA. It offers a tax-free return without market risk, adding another layer to a diversified financial plan. It's a way to secure the best life insurance policy for protection while ensuring your money comes back to you.
Actionable Tips for Policyholders
To determine if an ROP policy is the right fit for you, consider these strategies:
- Run the Numbers: Calculate the difference in premium between a standard term and an ROP policy. Then, project the potential growth if you invested that difference in a conservative fund or Roth IRA. This comparison will reveal the opportunity cost.
- Confirm Affordability: You must be confident you can afford the higher premiums for the entire term. Lapsing an ROP policy early often results in forfeiting a significant portion or all of your returned premiums.
- Understand Inflation's Impact: The money returned in 20 or 30 years will have less purchasing power than it does today. Factor this into your decision-making process.
- Evaluate Your Savings Habits: Be honest with yourself. If you are unlikely to save and invest the money you'd save with a standard term policy, the forced savings aspect of ROP might be highly beneficial.
Top 10 Life Insurance Policies Comparison
| Insurance Type | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements ⚡ | Expected Outcomes ⭐📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages 💡 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Term Life Insurance | Low 🔄 (simple underwriting and fixed term) | Low ⚡ (affordable premiums) | Death benefit if death occurs in term; no cash value; expires if outlived | Temporary financial obligations; young families; mortgage or income protection | Most affordable; straightforward; high coverage for low cost |
| Whole Life Insurance | Moderate 🔄 (permanent with cash value) | High ⚡ (significant monthly cost) | Lifetime coverage, guaranteed cash value growth; dividends possible | Estate planning; forced savings; retirement income supplement | Lifetime coverage; predictable returns; builds cash value |
| Universal Life Insurance | Moderate-High 🔄 (flexible premiums/death benefit) | Moderate ⚡ (higher than term, less than whole) | Lifetime coverage with adjustable premiums; cash value grows with interest | Variable income earners; those wanting premium flexibility | Flexible premiums/death benefits; potential cash value growth |
| Guaranteed Universal Life Insurance | Low-Moderate 🔄 (focused on death benefit) | Moderate ⚡ (lower than whole) | Permanent coverage with guaranteed premiums and death benefit; little/no cash | Estate planning; permanent coverage without cash value; affordable permanent | Most affordable permanent; guaranteed coverage and premiums |
| Variable Universal Life Insurance | High 🔄 (investment options, active management) | High ⚡ (highest premiums and fees) | Permanent coverage; cash value fluctuates with investment performance | Sophisticated investors; high income; willing to manage investments | High growth potential; investment control; flexible premiums |
| Indexed Universal Life Insurance | High 🔄 (complex caps, participation rates) | Moderate-High ⚡ | Cash value growth tied to market index with downside protection | Risk-averse seeking market-linked growth; retirement income supplement | Market upside with no downside; flexible; tax-deferred growth |
| Final Expense Life Insurance | Low 🔄 (simplified underwriting) | Low ⚡ | Small permanent coverage for final expenses; minimal cash value | Seniors; people with health issues; covering funeral/burial costs | Easy qualification; affordable small coverage; permanent and fast issue |
| Group Life Insurance | Low 🔄 (employer-provided, no underwriting) | Low ⚡ (often free or subsidized) | Basic term coverage linked to salary; ends or reduces upon job changes | Employees seeking basic coverage; supplement to individual insurance | No medical exam; free/low cost; automatic enrollment |
| No Medical Exam Term Life Insurance | Low 🔄 (simplified underwriting, no exam) | Low ⚡ (higher than term with exam) | Term coverage quickly issued with moderate coverage limits | Fast coverage needed; needle-phobic individuals; healthy younger applicants | Fast approval; no medical exam; convenient application |
| Return of Premium (ROP) Term Life | Low 🔄 (standard term with premium refund) | Moderate ⚡ (2-4x standard term cost) | Death benefit plus 100% premiums returned if outlived term | Savers lacking discipline; want forced savings with term protection | Premiums returned; forced savings; death benefit during term |
From Options to Action: Securing Your Ideal Policy
Navigating the landscape of life insurance can feel like learning a new language. You began this journey likely facing a wall of jargon and a dizzying array of options, but you are now equipped with the foundational knowledge to make a confident, strategic decision. We have unpacked ten distinct types of policies, from the straightforward protection of Term Life to the legacy-building potential of Whole Life and the market-driven flexibility of Variable Universal Life.
The core lesson is this: the quest for the best life insurance policy is not about finding a single, universally acclaimed product. Instead, it is a deeply personal process of matching the right financial tool to your unique circumstances, goals, and timeline. The ideal policy for a young family protecting a new mortgage (likely Term Life) is fundamentally different from the one best suited for a high-net-worth individual focused on estate planning (perhaps a form of Universal Life).
Synthesizing Your Knowledge into a Decision
Let's distill the key insights from our exploration into a clear decision-making framework. Your choice will ultimately hinge on the interplay between three critical factors: your purpose, your budget, and your timeline.
- For Pure Protection: If your primary goal is to provide the largest possible death benefit for the lowest initial cost to cover temporary needs like a mortgage or raising children, Term Life and No Medical Exam Term Life are your clear frontrunners. They offer simplicity and affordability, delivering on the core promise of life insurance without complexity.
- For Lifelong Certainty and Cash Value: For those seeking permanent coverage that will last their entire life, accompanied by a guaranteed cash value savings component, Whole Life and Guaranteed Universal Life (GUL) are the gold standard. They provide unwavering stability and a forced savings mechanism, ideal for legacy goals and final expense planning.
- For Flexible Premiums and Market Growth: If you desire more control over your policy's structure and have a higher risk tolerance, the Universal Life family (IUL, VUL) offers a compelling alternative. These policies allow you to adjust your premium payments and link your cash value growth to market indices or investment sub-accounts, offering greater potential rewards alongside greater risk.
Your personal financial situation dictates which of these categories makes the most sense. A self-employed professional may value the premium flexibility of a Universal Life policy, while a blue-collar worker might prioritize the ironclad guarantees of Whole Life for final expense coverage.
Your Actionable Roadmap to a Secure Future
Knowledge is only potential power; action is what transforms it into security for your loved ones. Simply understanding the difference between an IUL and a GUL is not enough. The next step is to translate this information into a tangible policy that protects your family.
Here is a simple, three-step process to move forward:
- Quantify Your Need: Before you even look at quotes, calculate your actual life insurance need. Use a simple formula: (Total Income to Replace x Years) + (Mortgage/Debts) + (College Costs) + (Final Expenses) – (Existing Savings/Assets). This number gives you a concrete coverage target.
- Compare the Market: Never settle for the first quote you see. The life insurance market is highly competitive, and pricing for the exact same coverage can vary significantly between carriers based on your specific age, health, and lifestyle. An online comparison tool is the most efficient way to get a panoramic view of your options.
- Consult an Independent Expert: While online tools are excellent for initial research, an independent agent can be an invaluable partner. They can help you "stress-test" your assumptions, navigate the underwriting process, and ensure the fine print of your chosen policy aligns perfectly with your long-term intentions.
Ultimately, securing the best life insurance policy is one of the most profound acts of financial responsibility you can undertake. It is a promise to your family that their lives can continue with stability and dignity, even if you are no longer there to provide for them. You have done the hard work of educating yourself. Now is the time to take that final, crucial step from deliberation to action and solidify that promise.
Ready to see how these policy types stack up for your specific needs? Use the free tools at My Policy Quote to instantly compare real-time rates from dozens of A-rated insurance carriers. Find your most affordable and effective coverage options in minutes by visiting My Policy Quote and get started on securing your family's future today.


